Grain trading is a vital component of the global food supply chain, as grains such as wheat, corn, and rice are staple foods for billions of people around the world. The Middle East, Canada, Turkey, Oman, and the UAE are all key players in the international grain trading market, with each country playing a unique role in the distribution and consumption of grains.
The Middle East is a major importer of grains, as the region has limited arable land and relies heavily on imports to meet its food needs. Countries such as Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Iran are among the largest importers of grains in the region, with a significant portion of these imports coming from countries like the United States, Russia, and Ukraine. The Middle East's dependence on grain imports makes it vulnerable to fluctuations in global grain prices, as any disruptions in the supply chain can have a significant impact on food security in the region.
Canada is one of the world's largest grain exporters, with wheat being the country's most important crop. The vast agricultural land in Canada allows for large-scale production of grains, which are primarily exported to countries in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. The Canadian grain trading market is known for its high-quality grains and efficient logistics, making it a reliable source of grains for importers around the world.
Turkey is another key player in the global grain trading market, as the country is both a major importer and exporter of grains. Turkey's strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia makes it an important hub for the transportation and distribution of grains to neighboring countries. The Turkish government also plays a role in regulating the grain trading market to ensure food security and control prices for consumers.
Oman and the UAE are both major importers of grains, as the arid climate in these countries limits agricultural production. These countries rely on imports to meet their food needs, with a significant portion of grains coming from countries in the region such as Iran, Saudi Arabia, and India. The grain trading market in Oman and the UAE is characterized by a high level of competition among traders, who compete to supply grains to local markets at competitive prices.
In conclusion, grain trading is a complex and interconnected global market that plays a crucial role in ensuring food security for billions of people around the world. The Middle East, Canada, Turkey, Oman, and the UAE are all key players in the international grain trading market, each playing a unique role in the distribution and consumption of grains. As global demand for grains continues to rise, these countries will play an important role in meeting the world's food needs and ensuring a stable supply of grains for consumers.

Edible oil is a staple ingredient in cuisines around the world, and its trade plays a significant role in the global economy. The Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey are all key players in the global trade of edible oil, both as importers and exporters.
The Middle East is a major importer of edible oil, given the region's reliance on imports to meet its domestic demand. Saudi Arabia, for example, is one of the largest importers of edible oil in the world, importing significant quantities of palm oil and soybean oil. Other countries in the region, such as the UAE and Qatar, also rely heavily on imported edible oil to meet their food needs. The Middle East's demand for edible oil is expected to continue growing in the coming years, driven by population growth and changing dietary preferences.
On the other hand, countries like Oman and Turkey are major exporters of edible oil. Oman, for example, exports significant quantities of sunflower oil, palm oil, and soybean oil to markets around the world. The country's strategic location at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe makes it a key player in the global edible oil trade. Similarly, Turkey is a major exporter of olive oil, one of the most sought-after varieties of edible oil in the world. Turkish olive oil is renowned for its quality and is exported to markets in Europe, the Middle East, and beyond.
Canada is another key player in the global trade of edible oil, particularly canola oil. Canada is the world's largest producer of canola, a versatile oilseed crop that is widely used in cooking and food processing. The country exports significant quantities of canola oil to markets around the world, including the US, Europe, and Asia. Canada's reputation for producing high-quality canola oil has made it a sought-after supplier in the global edible oil market.
The UAE, on the other hand, is a major re-exporter of edible oil, given its strategic location as a hub for trade and commerce in the Middle East. The country imports edible oil from various regions, such as Southeast Asia and the Americas, and re-exports it to markets in the Middle East and beyond. The UAE's role as a re-exporter of edible oil has helped to drive growth in the country's food processing and trading sectors.
The global trade of edible oil is a complex and dynamic market, with countries like the Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey playing key roles as importers and exporters. The growing demand for edible oil, driven by population growth and changing dietary preferences, is expected to further fuel the trade of this essential food commodity in the coming years. These countries will continue to play a crucial role in ensuring that the world's supply of edible oil meets the needs of consumers around the globe.

Nuts are one of the most popular and widely consumed snacks in the world. They are not only delicious but also packed with essential nutrients such as protein, healthy fats, vitamins, and minerals. The global trade of nuts has been thriving in recent years, with an increasing demand for these healthy snacks across various regions.
One of the largest producers and exporters of nuts in the world is the United States. The country produces a wide variety of nuts including almonds, walnuts, pistachios, and pecans. These nuts are exported to various countries around the world, particularly in the Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey.
The Middle East is a significant market for nuts, particularly for pistachios and almonds. Countries in this region such as Saudi Arabia, Iran, and Turkey are major importers of nuts from the United States. The demand for nuts in the Middle East is driven by the growing awareness of the health benefits of nuts and the increasing popularity of snacking among consumers.
Canada is also a prominent player in the global trade of nuts. The country produces a variety of nuts such as hazelnuts, cashews, and macadamia nuts. Canadian nuts are highly sought after for their quality and taste. Canada is both an importer and exporter of nuts, with a significant portion of its nut exports going to countries in the Middle East, particularly UAE and Oman.
Oman and UAE are emerging markets in the nut trade industry. These countries have shown a growing interest in importing nuts from various suppliers around the world. Nuts are increasingly being incorporated into the diets of consumers in Oman and UAE, as people become more health-conscious and are looking for nutritious snack options.
Turkey, on the other hand, is a major producer and exporter of nuts in the world. The country is renowned for its high-quality hazelnuts, which are in high demand globally. Turkish hazelnuts are exported to countries in the Middle East, Europe, and North America. Turkey also imports nuts from other countries to meet its domestic demand.
The global trade of nuts is a thriving industry with countries like the United States, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey playing significant roles as both producers and consumers of nuts. The demand for nuts is expected to continue growing as consumers become more health-conscious and look for nutritious snack options. The trade of nuts not only benefits the economies of the countries involved but also provides consumers with access to a wide variety of delicious and nutritious nuts from around the world.

Global trade of seeds plays a crucial role in ensuring food security and sustaining agricultural production worldwide. Seeds are the foundation of agriculture, as they are essential for growing crops that provide food, feed, fiber, and fuel for human and animal consumption. The global seed trade involves the import and export of various types of seeds, including cereal crops, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and oilseeds, among others. In this essay, we will explore the trends in global seed trade and the specific trade dynamics in the Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey.
The global seed trade has experienced significant growth over the past few decades, driven by increasing demand for high-quality seeds, technological advancements in seed breeding and production, and expanding global agricultural markets. According to the International Seed Federation (ISF), the global seed trade has grown steadily, with the total value of seed exports reaching $20 billion in 2020. Major seed exporting countries include the United States, the Netherlands, France, Germany, and China, while major seed importing countries include Brazil, Mexico, India, Pakistan, and Japan.
In the Middle East, the seed trade is influenced by the region's arid climate and limited agricultural land, which necessitates the importation of a significant portion of the seeds needed for crop production. Major seed importing countries in the Middle East include Saudi Arabia, Egypt, Iran, Turkey, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE). These countries import a wide range of seeds, including wheat, barley, corn, rice, fruits, and vegetables, from countries like the United States, China, India, and Europe.
Canada is a major player in the global seed trade, with a reputation for producing high-quality seeds, particularly for cereals, oilseeds, and pulses. As one of the world's largest exporters of agricultural products, Canada exports seeds to various countries worldwide, including the United States, China, Mexico, Japan, and Europe. Major Canadian seed exports include canola, wheat, soybeans, barley, and corn, which are essential for food and feed production.
Oman, UAE, and Turkey are also important players in the global seed trade, albeit with different trade dynamics. Oman, due to its limited agricultural land and water resources, relies heavily on seed imports for crop production. The country imports a diverse range of seeds, including fruits, vegetables, cereals, and forages, from countries like India, Pakistan, Europe, and Africa. UAE, on the other hand, imports a significant amount of seeds for horticultural crops and landscaping purposes, mainly from Europe, India, China, and the United States. Turkey, as a key player in the region's agricultural sector, both imports and exports seeds, particularly for cereals, oilseeds, and pulses. The country exports seeds to various countries in the Middle East, Europe, and Africa, while importing seeds for crop production and breeding purposes.
In conclusion, the global trade of seeds is essential for ensuring food security, promoting agricultural sustainability, and supporting economic development worldwide. The Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey are all important players in the global seed trade, with unique trade dynamics shaped by their agricultural needs, climate conditions, and trade policies. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for high-quality seeds will only increase, emphasizing the need for sustainable seed trade practices and collaborations to meet the world's agricultural challenges.

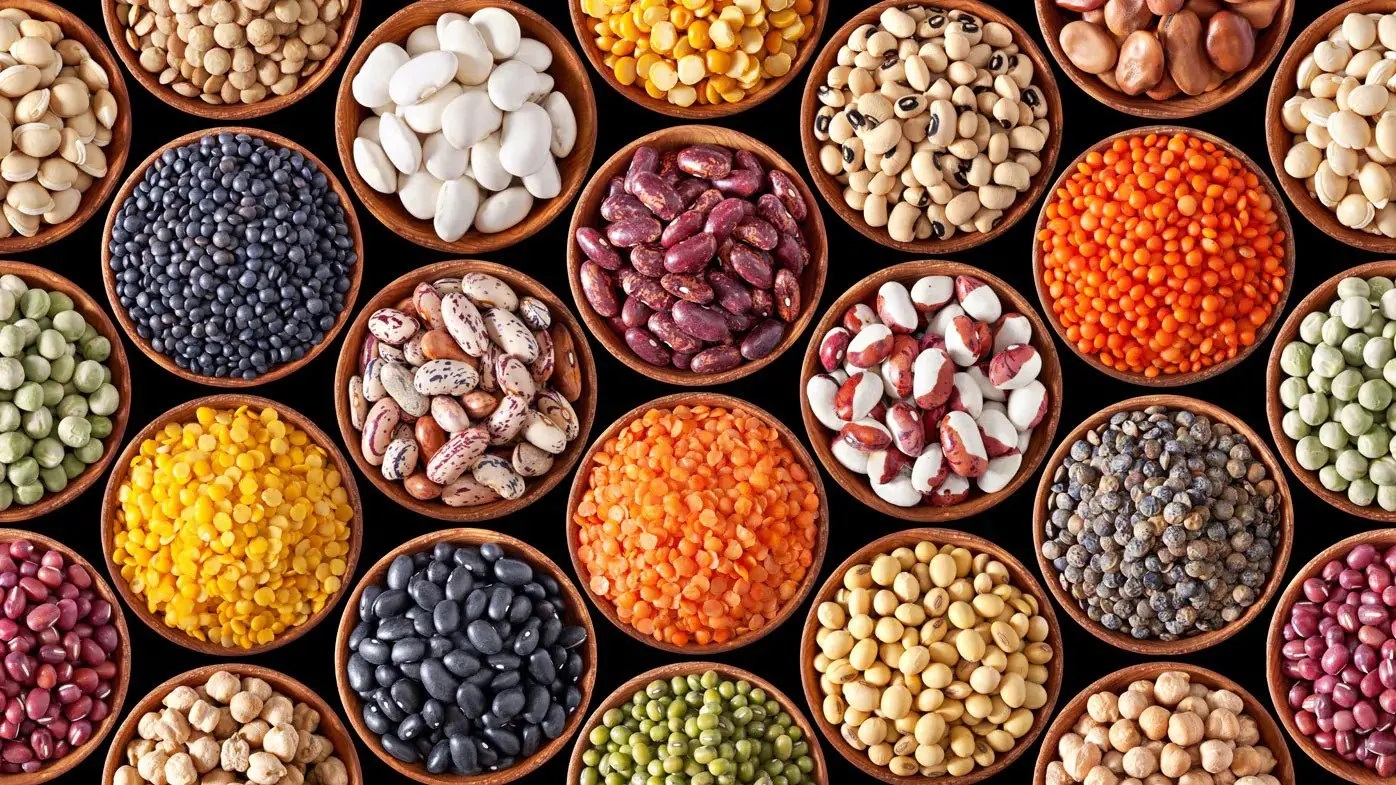
Pulses are a vital source of protein and essential nutrients for millions of people around the world. As a result, global trade of pulses has become increasingly important in ensuring food security and meeting the nutritional needs of various populations. In this essay, we will delve into the global trade of pulses, with a focus on the Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey.
The Middle East is a major importer of pulses, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Egypt, and Iran being the largest importers in the region. The Middle East relies heavily on imports to meet its domestic demand for pulses, as the region has limited arable land suitable for pulse cultivation. The demand for pulses in the Middle East is driven by its growing population, changing dietary preferences, and the need to diversify food sources.
Canada is one of the largest exporters of pulses in the world, with lentils, chickpeas, and dry peas being the major exports. Canada's pulse exports are highly sought after due to their high quality and reliability. The country benefits from its large and fertile agricultural land, advanced farming techniques, and favorable climatic conditions for pulse cultivation. Canada's pulse exports play a crucial role in meeting the global demand for pulses and contributing to food security worldwide.
Oman, UAE, and Turkey are also significant players in the global pulse trade. Oman and UAE are major importers of pulses, as they rely on imports to meet their domestic demand for pulses. These countries import pulses from various sources, including Canada, India, and Australia, to ensure a steady supply of pulses to their populations. Turkey, on the other hand, is both an importer and exporter of pulses. The country produces a variety of pulses, such as lentils, chickpeas, and beans, for domestic consumption and export. Turkey's pulse exports are valued for their high quality and competitive prices, making them popular in international markets.
Overall, the global trade of pulses plays a crucial role in ensuring food security, meeting the nutritional needs of diverse populations, and promoting economic development. Countries in the Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey are key players in the global pulse trade, with each contributing to the supply chain in their unique way. As the demand for pulses continues to rise, it is essential for countries to collaborate and support each other to ensure a stable and sustainable global pulse trade system. By doing so, we can work towards a future where pulses are readily available and accessible to all, contributing to a healthier and more food-secure world.

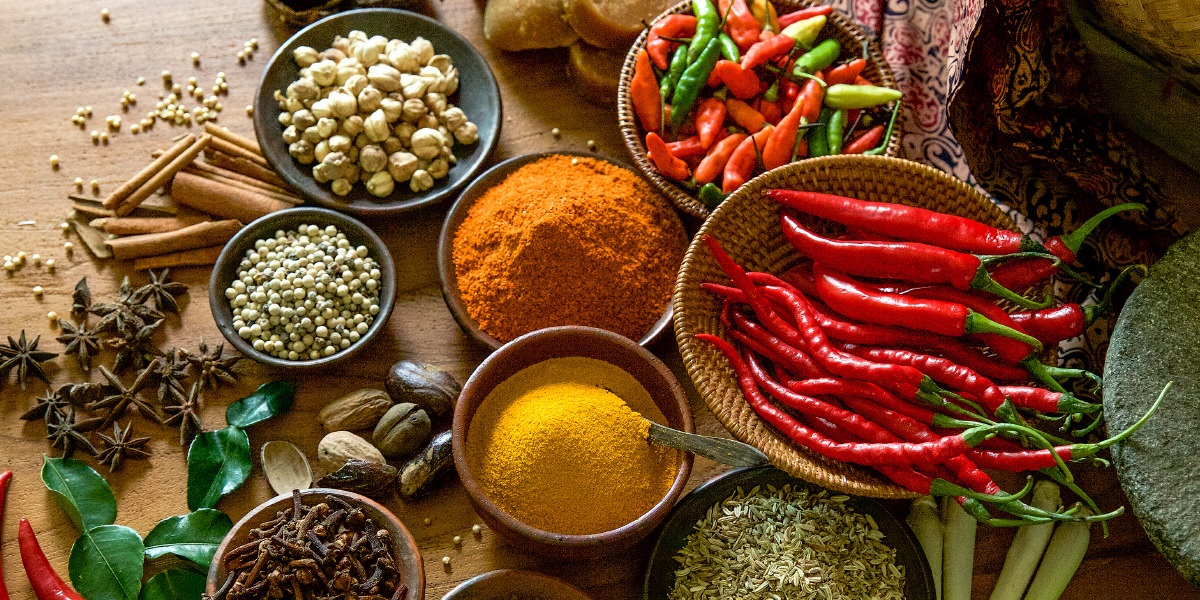
Spices have been an integral part of global trade for centuries, with their use dating back to ancient times. The trade of spices has played a crucial role in shaping world history and economy. Today, the global spice trade is booming, with countries like Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey playing a significant role in both the import and export of spices.
The Middle East has always been a hub for spice trade, owing to its geographical location at the crossroads of Asia, Europe and Africa. Countries like India, Sri Lanka and Indonesia are major exporters of spices to the Middle East, where they are in high demand for use in traditional Middle Eastern cuisine. The Middle East also exports a variety of spices like saffron, sumac, and za'atar to other parts of the world.
Canada is another important player in the global spice trade. With a diverse population that appreciates a wide range of cuisines, Canada imports a variety of spices from countries like India, China, and Mexico. In recent years, there has been a growing demand for exotic and gourmet spices in Canada, leading to an increase in imports from countries like Madagascar and Morocco.
Oman, UAE and Turkey are also important players in the global spice trade. Oman, located on the Arabian Peninsula, is a major exporter of frankincense and myrrh, both of which have been used in traditional medicine and religious ceremonies for centuries. The UAE, with its cosmopolitan population, imports a wide range of spices from around the world, which are used in the country's diverse culinary scene. Turkey, on the other hand, is known for its production of spices like cumin, sumac, and paprika, which are exported to countries in Europe and the Middle East.
Overall, the global spice trade is a thriving industry, with countries like Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey playing a crucial role in both the import and export of spices. As demand for exotic and gourmet spices continues to rise, we can expect the spice trade to grow even further in the years to come.

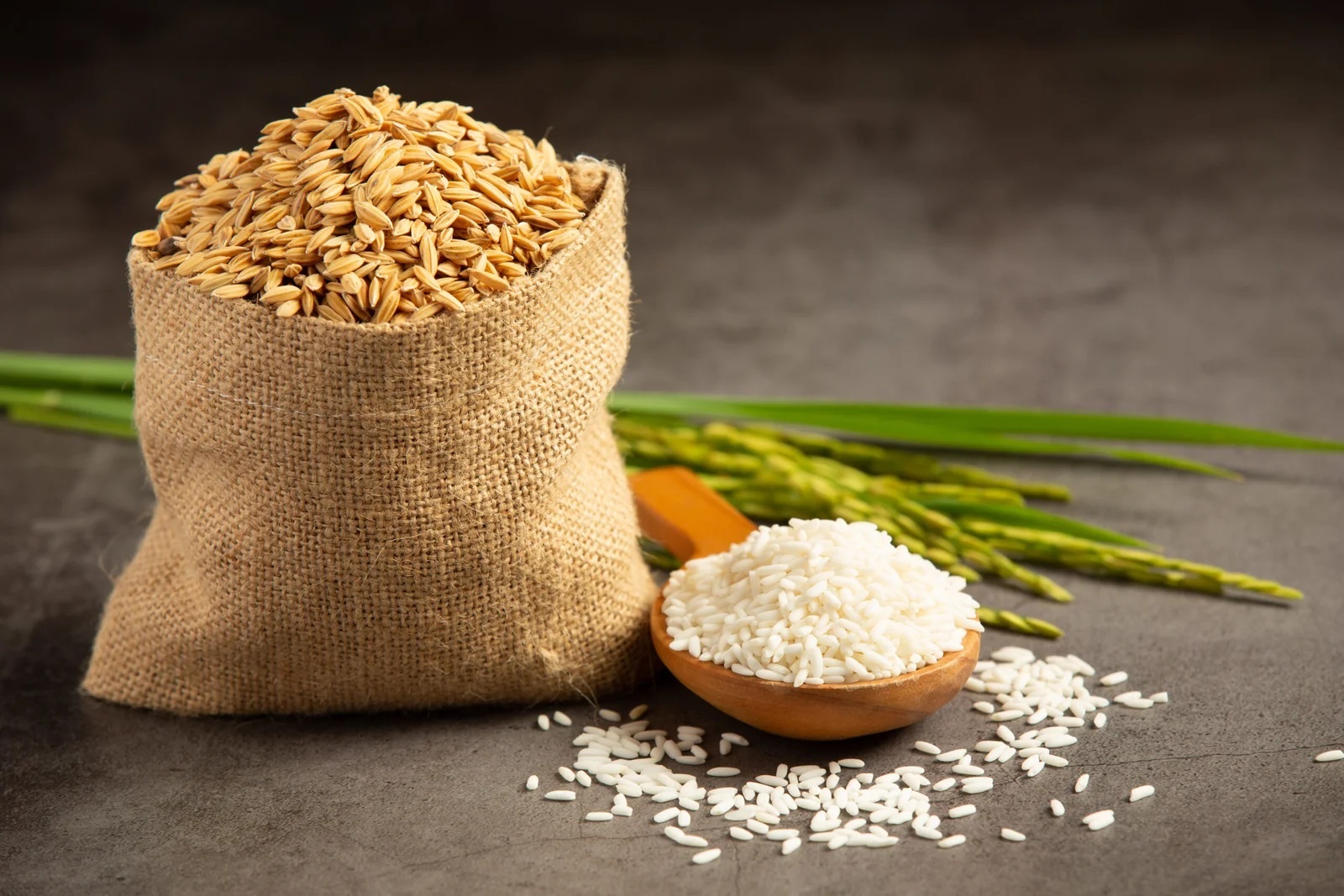
Rice is one of the most important staple foods in the world, and its global trade plays a crucial role in food security and economic development. As populations continue to grow, the demand for rice will increase, making it essential to understand the dynamics of global rice trade.
The global rice market is characterized by a complex network of importers and exporters, with several key players driving international trade. Some of the major rice exporters in the world include countries such as India, Thailand, Vietnam, Pakistan, and the United States. These countries have large production capacities and are able to export significant quantities of rice to various regions around the world.
On the other hand, countries like Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey are major importers of rice due to their limited domestic production capabilities. These countries rely heavily on rice imports to meet the demands of their populations, making global rice trade a critical component of their food security strategies.
The Middle East is one of the largest importers of rice in the world, with countries like Saudi Arabia, Iraq, and Kuwait being major players in the global rice market. These countries import rice primarily from Asian countries such as India, Pakistan, and Thailand, as well as from the United States and other regions. The demand for rice in the Middle East is fueled by a growing population and changing dietary habits, making it essential for these countries to maintain a steady supply of rice through imports.
Canada, Oman, UAE, and Turkey are also significant importers of rice, with each country having its own unique set of factors driving rice imports. Canada, for example, imports rice to meet the demands of its multicultural population, which includes various ethnic groups that consume rice as a staple food. Oman, UAE, and Turkey, on the other hand, import rice to supplement their domestic production and meet the demands of their populations.
In recent years, the global rice market has been influenced by various factors such as climate change, trade policies, and geopolitical tensions. These factors have led to fluctuations in rice prices and trade volumes, making it essential for countries involved in the global rice trade to adapt to changing market conditions.
Overall, the global trade of rice plays a crucial role in ensuring food security and economic development in countries around the world. As populations continue to grow and dietary habits evolve, the importance of global rice trade will only continue to increase, making it essential for countries to work together to ensure a stable and reliable supply of rice for all.

Chemical products are an essential component of global trade, as they are used in various industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, construction, and manufacturing. The global trade of chemical products has been on the rise in recent years, with countries like the United States, China, and Germany being among the top exporters.
In the Middle East, countries like Saudi Arabia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) are key players in the global trade of chemical products. Saudi Arabia, for example, is a major exporter of petrochemical products, as it has one of the largest oil reserves in the world. Iran is also a significant exporter of chemical products, particularly in the areas of fertilizers, plastics, and pharmaceuticals.
Among the Middle Eastern countries, the UAE stands out as a major hub for the global trade of chemical products. The country's strategic location and world-class infrastructure make it an attractive destination for chemical companies looking to establish a presence in the region. The UAE is known for its extensive network of free trade zones, which offer numerous incentives to foreign investors, including 100% foreign ownership, tax exemptions, and no currency restrictions.
In terms of imports, countries in the Middle East rely heavily on chemical products from countries like the United States, Germany, and China. These countries are known for their advanced technology and high-quality chemical products, making them preferred suppliers for many Middle Eastern countries.
Moving on to Canada, the country is also a significant player in the global trade of chemical products. Canada is known for its thriving chemical industry, which includes the production of petrochemicals, fertilizers, and pharmaceuticals. The country's close proximity to the United States, its largest trading partner, has helped facilitate the exchange of chemical products between the two countries.
In Oman, the chemical industry is still in its nascent stages, but the country has been making efforts to diversify its economy and promote the growth of the sector. Oman is rich in natural resources, including oil and natural gas, which can be used as feedstock for the production of chemical products. The government has implemented various initiatives to attract foreign investment in the chemical sector, including tax incentives and streamlined regulations.
In the UAE, chemical products are among the top exports of the country, with key products including plastics, fertilizers, and pharmaceuticals. The UAE’s strategic location, well-developed infrastructure, and business-friendly environment have made it an attractive destination for chemical companies looking to expand their global reach.
Finally, Turkey is also a major player in the global trade of chemical products, with the country being a key exporter of chemicals to countries in Europe, the Middle East, and North Africa. Turkey’s chemical industry is known for its diversity, with products ranging from petrochemicals and plastics to pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals. The country’s strategic location at the crossroads of Europe and Asia, as well as its well-established manufacturing base, make it an important player in the global chemical trade.
The global trade of chemical products is a vital component of the global economy, with countries like the UAE, Canada, Oman, and Turkey playing pivotal roles in the exchange of chemical products around the world. The Middle East, in particular, is a key region for the production and trade of chemical products, with countries in the region benefiting from their strategic locations, natural resources, and supportive government policies. As the demand for chemical products continues to grow, these countries are poised to capitalize on the opportunities presented by the global chemical trade.


Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC is a leading company specializing in the trading of various food and beverage products such as grains, oils, nuts, seeds, pulses, spices, rice, and chemical products. With a strong presence in countries like Canada, Turkey, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE), the company has established itself as a reliable and reputable player in the global trading arena.
The company's focus on quality and customer satisfaction has enabled it to build a loyal customer base in these countries. By sourcing products from trusted suppliers and ensuring stringent quality control measures, Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC has been able to deliver premium products to its customers consistently.
One of the key products that the company trades in is grains. With a growing demand for grains worldwide, particularly in countries like Canada and Turkey, Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC has been able to cater to this demand by offering a wide range of grains such as wheat, corn, barley, and rice. The company ensures that these grains are of the highest quality and are sourced from reliable suppliers to meet the diverse needs of its customers.
In addition to grains, the company also specializes in the trading of oils, nuts, seeds, and pulses. These products are essential ingredients in various cuisines and are in high demand in countries like Oman and the UAE. Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC ensures that these products are sourced from reputable suppliers and are of the highest quality, meeting the stringent standards set by its customers.
Spices are another key product in the company's portfolio. With a wide range of spices sourced from different regions around the world, Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC has been able to cater to the diverse culinary preferences of its customers in Canada, Turkey, Oman, and the UAE. The company ensures that these spices are of premium quality, imparting rich flavors and aromas to the dishes they are used in.
Rice is another important product that the company trades in. With a growing demand for rice in countries like Oman and the UAE, Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC offers a wide variety of rice, including basmati, jasmine, and long-grain rice. The company ensures that the rice it trades in is of superior quality, meeting the expectations of its discerning customers.
Chemical products are also a part of the company's trading portfolio. With a focus on quality and safety, Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC ensures that the chemical products it trades in meet the highest standards set by regulatory authorities. By sourcing these products from trusted suppliers, the company guarantees the quality and reliability of these products to its customers.
In conclusion, Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC has established itself as a reputable player in the global trading of food and beverage products. With a strong focus on quality, customer satisfaction, and reliability, the company has been able to build a loyal customer base in countries like Canada, Turkey, Oman, and the UAE. By offering a wide range of products such as grains, oils, nuts, seeds, pulses, spices, rice, and chemical products, Nimex Hub Food & Beverages Trading Co. L.LC continues to meet the diverse needs of its customers and set itself apart in the competitive global trading market.
Discover the Thriving World of Grain Trading
The world of grain trading is a thriving and complex ecosystem that plays a crucial role in the global economy. From the humble origins of farming and agriculture, the trade of grains has evolved into a sophisticated market that spans continents and influences everything from food prices to international relations. In this essay, we will explore the fascinating world of grain trading, its history, key players, and the factors that drive its growth.
Grain trading has been around for centuries, dating back to the dawn of organized agriculture. As societies developed and populations grew, the need for a reliable and efficient way to exchange grains became apparent. Ancient civilizations such as the Egyptians and Mesopotamians relied on grain as a staple food source and used barter systems to trade with neighboring communities.
Fast forward to the modern era, and grain trading has become a multi-billion dollar industry that affects billions of people around the world. The key players in the grain trading market are multinational corporations, agricultural cooperatives, governments, and speculators. These entities buy, sell, and transport grains such as wheat, corn, and rice across borders and continents, often in massive quantities.
The factors that drive the growth and volatility of the grain trading market are diverse and complex. Weather patterns, government policies, and consumer demand all play a role in determining grain prices. Natural disasters such as droughts, floods, and pests can devastate crops and disrupt the supply chain, leading to price spikes and shortages. Government subsidies and regulations can also impact grain trading, as can geopolitical tensions and trade disputes between countries.
Despite the challenges and risks involved, grain trading remains a lucrative and essential industry that feeds billions of people around the world. The global demand for grains continues to rise as populations grow and diets change. As a result, there is a constant need for innovation and efficiency in the grain trading market, from developing new technologies to improve crop yields to building stronger supply chains to meet the growing demand.
In conclusion, the world of grain trading is a complex and dynamic market that plays a vital role in the global economy. From its ancient origins to its modern-day complexities, grain trading has evolved into a thriving industry that feeds billions of people and drives economic growth. As the world continues to change and develop, the importance of grain trading will only continue to grow, making it a fascinating and essential sector to watch and explore.
From Farm to Market: The Art of Trading High Quality Grains and Seeds
Agriculture has played a crucial role in human civilization since the beginning of time. The cultivation of grains and seeds has been a fundamental part of human sustenance, providing us with the necessary nutrients and energy to survive and thrive. The journey of grains and seeds from the farm to the market is a complex process that requires careful planning, attention to detail, and hard work. In this essay, we will explore the art of trading high-quality grains and seeds, from cultivation to consumption.
The process of trading high-quality grains and seeds begins on the farm, where farmers work tirelessly to cultivate and harvest their crops. High-quality grains and seeds require careful attention to detail, from selecting the right variety of seeds to planting them at the optimal time and ensuring that they receive the necessary nutrients and water. Farmers must also monitor their crops closely to protect them from pests and diseases, as any damage can significantly impact the quality of the final product.
Once the grains and seeds have been harvested, they are typically transported to a processing facility where they are cleaned, sorted, and packaged for sale. The quality of the grains and seeds is crucial at this stage, as any contaminants or foreign matter can affect the taste, appearance, and nutritional value of the final product. Processing facilities must adhere to strict quality control measures to ensure that only the highest quality grains and seeds are sent to market.
From the processing facility, high-quality grains and seeds are typically transported to wholesalers or distributors who then sell them to retailers and consumers. The trading of grains and seeds involves a complex network of producers, processors, wholesalers, and retailers, all working together to ensure that the final product reaches the consumer in a timely and efficient manner. Factors such as transportation, storage, and pricing all play a role in the trading process, and each step must be carefully managed to ensure that the grains and seeds maintain their quality and freshness.
One of the key challenges in trading high-quality grains and seeds is ensuring that they reach the market in optimal condition. Grains and seeds are perishable commodities that can spoil quickly if not stored and handled correctly. Therefore, it is essential for traders to have proper storage facilities, transportation systems, and packaging materials to preserve the quality of the product. Additionally, traders must be aware of market demand and pricing trends to ensure that they can sell their products at a competitive price.
In conclusion, the trading of high-quality grains and seeds is a complex and intricate process that requires careful planning, attention to detail, and hard work. From cultivation to consumption, farmers, processors, wholesalers, and retailers all play a crucial role in ensuring that the grains and seeds reach the market in the best possible condition. By following best practices in crop cultivation, processing, and trading, we can continue to enjoy high-quality grains and seeds that nourish our bodies and sustain our civilization.

This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.
 Global trade of Spices in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
Global trade of Spices in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
 Global trade of Grain in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
Global trade of Grain in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
 Global trade of Seeds in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
Global trade of Seeds in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
 Global trade of Pulses in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
Global trade of Pulses in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
 Global trade of Nuts in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
Global trade of Nuts in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
 Global trade of Rice in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)
Global trade of Rice in the world, Middle East, Canada, Oman, UAE and Turkey (import and export)